Fortune Procurators is your India purchasing office without ever being here. We reach those suppliers that don’t appear in your searches.
6, Ganga Bhagyoday, E Ward,Kasaba Bawada, Kolhapur
Call Us: +91 9158 88 2095
Tuesday - Sunday
(9.30am - 6.10pm)

It is a method for producing casting in a sand mold. Following castings can be obtained by sand casting.
1. Steel;
2. Iron;
3. Non ferrous
1. suitable for making blanks with complex shapes, complex inner cavity.
2. Wide adaptability.
3. Material with poor plasticity sand casting is the only forming process for manufacturing its parts.
1. Automotive engine block;
2. Cylinder head; 3. Crankshaft etc...

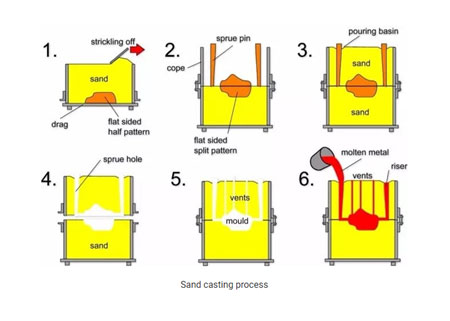
Process
A kind of casting method that usually refers to making patterns in fusible materials, covering surface of the pattern with several layers of refractory materials, & then melting the pattern out of the mold shell to obtain a mold without a parting surface , which can be filled after baking at high temperature.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Application |
| 1. High dimensional & geometric accuracy. | 1. Complicated procedure | 1. For production of small parts with complex shapes, high precision requirement |
| 2. High surface roughness. | 2. High Cost | 2. Turbine engine blade |

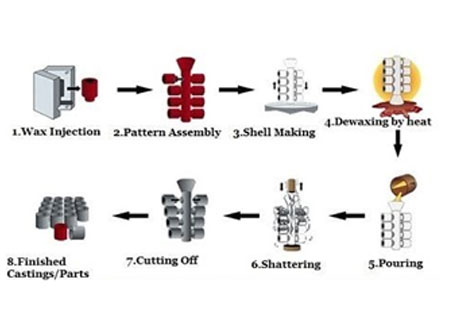
Process
High pressure metal liquid is pressed into a precision metal mold cavity at high speed, & the metal liquid is cooled & solidified under pressure to form a casting.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Application |
| 1. Metal liquid is subjected to high pressure & flow rate is fast during die casting. | 1. Casting is prone to produce fine pores & shrinkage. | 1. Automotive industry |
| 2. Good product quality, stable size & good interchangeability | 2. Low plasticity & should not work under impact load & vibration. | 2. Instrument Industry |
| 3. High production efficiency. | 3. At high melting point, life of the mold is low, which affects the expansion of die casting. | 3. Agricultural machinery. |
| 4. Mold can be used many times. | 4. Machine tool industry. | |
| 5. Suitable for mass production & good economic benefits. | 5. Electronic, national defense industry. | |
| 6. Medical equipments. |

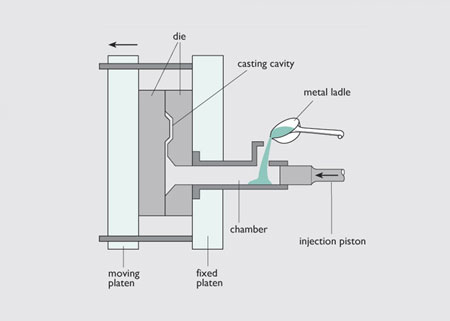
Process
In this method of making liquid metal fill a mold under a low pressure (0.02-0.06MPa) & crystallize under pressure to form a casting.
| Characteristics | Application |
| 1. Pressure & speed during pouring can be adjusted; it can be applied to various casting molds, various alloys & various sizes. | Mainly used in traditional products (cylinder head, hub, cylinder frame) |
| 2. Eliminate the need to fill up the riser & increase the metal utilization rate to 90 -98%. | |
| 3. Low labor intensity, good labor conditions, simple equipment. |

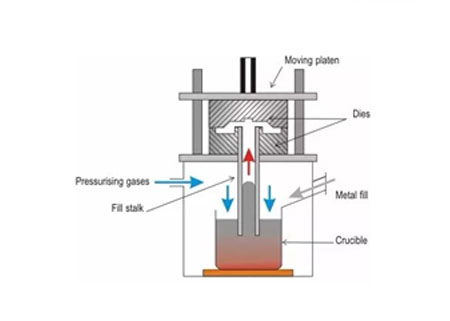
Process
In this method molten metal is poured into a rotating mold, & the mold is filled & solidified under the action of centrifugal force.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Application |
| 1. No metal consumption in the pouring & the riser system, which improves process yield. | 1. Limitations when used in the production of special shaped casting. | 1. Cast pipes. |
| 2. High density, few defects (pores & slag inclusion) | 2. Prone to specific gravity segregation. | 2. Produce steel, iron & non ferrous carbon alloy castings. |
| 3. High mechanical properties. | 3. Engine cylinder liners. | |
| 4. Easy to manufacture composite metal casting of barrels & sleeves. | 4. Shaft sleeve. |
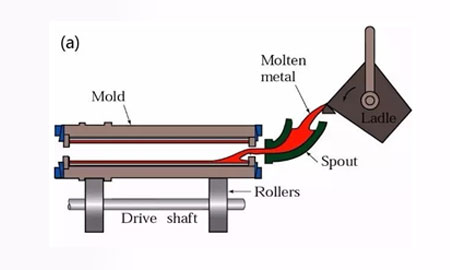
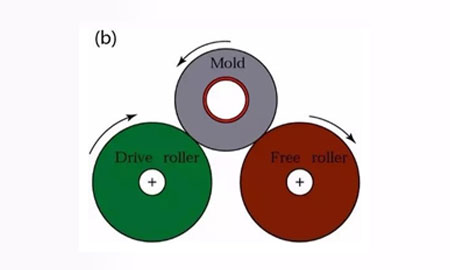
In this method liquid metal is filled with a metal mold under action of gravity & cooled & solidified in the mold to obtain a casting.
| Advantage | Disadvantage | Application |
| 1. Large thermal conductivity & heat capacity. | 1. Longer manufacturing & higher cost | 1. Large scale production of non ferrous castings. |
| 2. Mechanical properties about 15% higher than sand casting. | 2. cracks are easy to occur when the casting is solidified. |

It is an advance die casting process that improves mechanical properties & surface quality of die casting parts by removing or significantly reducing the pores & dissolved gases in the die-casting part by extracting the gas in the die-casting mold cavity during the die-casting process.
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| 1. Eliminate air holes inside the die casting. | 1. Mold sealing structure is complicated. Making & installing is difficult. Cost is high. |
| 2. Improves the mechanical properties, surface quality of the die casting. | |
| 3. Improves the filling conditions, can cast inner casting. |

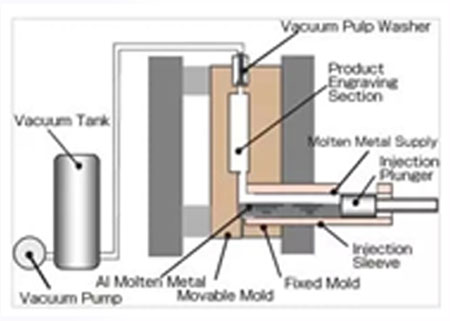
Process
It is a method for solidifying liquid or semi old metal under high pressure & flowing forming to directly obtain the product or blank. It has the advantage of high utilization rate of liquid metal, simplified process & stable quality. It is an energy saving metal forming technology with potential application prospects.
1. Eliminate internal pores, shrinkage & other defects.
2. Low surface roughness & high dimensional accuracy.
3. It can prevent the occurrence of casting cracks.
4. Easy to realize mechanization & automation.
1. Used to produce various types of alloys such as aluminium, zinc, copper, nodular cast iron etc…

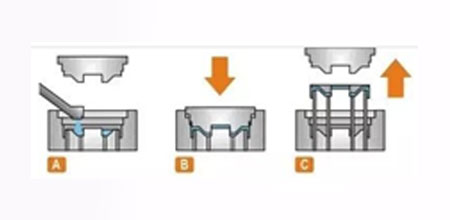
Process
It is new casting method that a combination of paraffin or foam models similar to the size & shape of the casting to form a model cluster. After brushing & drying the refractory coating, it is buried in dry quartz sand to vibrate. Pouring under negative pressure to vaporize model, the liquid metal occupies the model position, & is formed after solidification & cooling.
1. High precision casting, no sand core, reducing processing time.
2. No parting surface, flexible design & high degree of freedom.
3. Clean production without pollution.
4. Reduce investment & production cost.
1. Suitable for the production of various sizes of precision castings with complex structure.

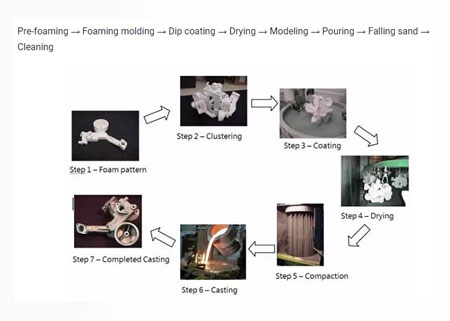
Process
It is an advance casting method. Its principle is to continuously pour molten metal into a special metal mold called a crystallizer. The solidified casting is continuously pulled out from the other end of the mold, & it can be obtain any length or specific length of casting.
1. Good mechanical properties, because metal is rapidly cooled, crystal are dense , structure is uniform.
2. Save metal & improve yield.
3. Simple procedure, eliminate molding & other procedures.
4. Continuously casting production is easy. Improve production efficiency.
Used to cast steel, iron, copper alloys, aluminium alloys, magnesium alloys.
| SN | Ferrous Metals | Non Ferrous metals |
| 1 | Steel | Aluminium & its alloys |
| 2 | Carbon Steel | Copper & its alloys |
| 3 | Alloy Steel | Lead |
| 4 | Cast iron | Zinc |
| 5 | Wrought Iron | Tin |


Process